
10
Scientific Facts About
Neurotransmitters that you Might Not Know
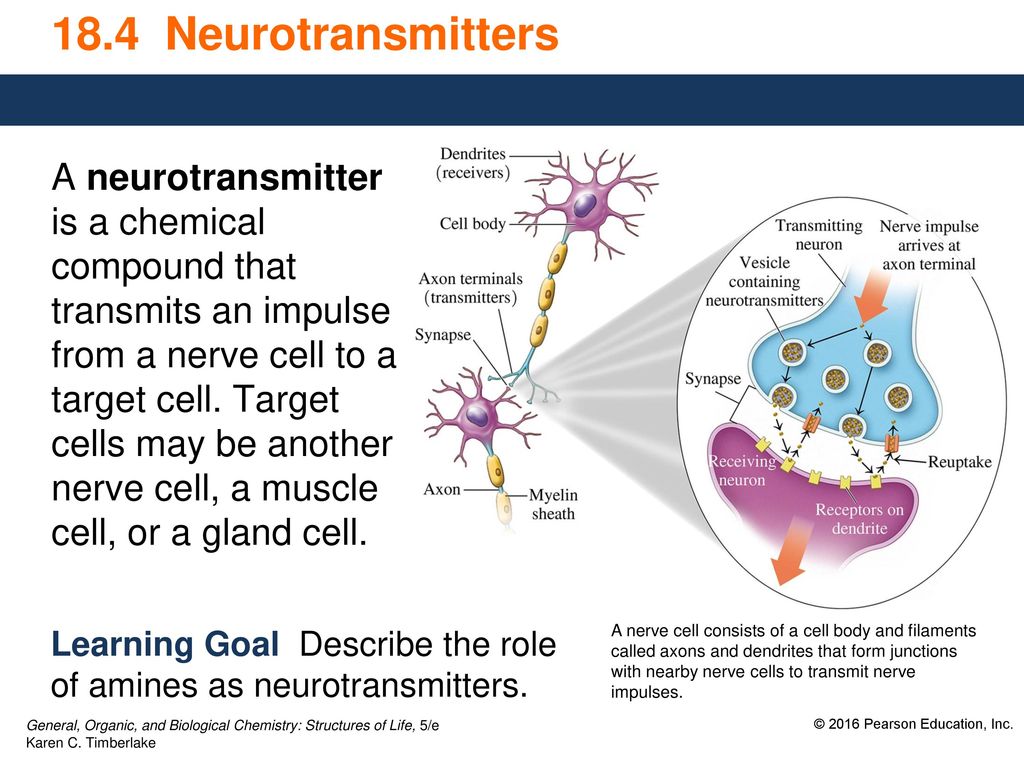
Neurotransmitters
also referred as chemical messengers, assist the brain in managing the tissues
and functions of the body through muscles and organs.
1.
There are more
than 100 types of chemical messengers in the body.
2.
Large proteins
usually size around 10nm, this means that normally neurotransmitters would size
around 0.5 to 5 nanometers.
3. Glutamate is the most
abundant neurotransmitter found.
4.
The first
neurotransmitter to be discovered is Acetylcholine. It is a kind of
neurotransmitter which is mainly responsible for activating muscles.
5.
Dopamine is
another major neurotransmitter responsible for monitoring the memory and motor
control. When the level of dopamine is elevated it may result in
hyperactivity and anxiety. It may further experience mood swings, attention
disorders, autism etc. Dopamine injections are used to recover the conditions
occurred when you are in shock or the conditions which are caused by surgery,
trauma or kidney failure.
6.
Norepinephrine is
an excitatory chemical messenger that is majorly responsible for processes of
focus and attention. It is also known as the stress hormone.
7.
GABA is a kind of
inhibitory neurotransmitter; it is a significant neurotransmitter that aids the
conversion of messages between nervous system and brain. The main function of
GABA is to reduce excitability, improve sleep and decrease inflammation.
8.
Epinephrine is
another excitatory neurotransmitter that regulates metabolism and blood
pressure. It functions primarily to raise glucose levels in the blood.
9.
Glutamate is a
chemical that is used by nerve cells to send signals to other cells. It is
considered as the major mediatory of the signals in CNS and is equally involved
in the brain functioning including memory, cognition, and learning.
10. Glycine is present in the brain stem and spinal cord
and participates in sensor and motor functions. Glycine act as a building block
for protein.
Name all the eight neurotransmitters
mentioned. What effect do they have on us?
Can you name any more
neurotransmitters?


No comments:
Post a Comment